How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate surveying missions. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, covering everything from understanding regulations and choosing the right equipment to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning visuals. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone technology, safety protocols, and best practices, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll navigate the complexities of FAA regulations, ensuring you comply with all legal requirements. We’ll also equip you with the practical skills to handle your drone with precision and confidence, from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. This comprehensive guide is your passport to the exciting world of drone piloting.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety protocols. Failure to do so can lead to accidents, fines, and legal repercussions. This section details crucial aspects of safe drone operation, including FAA regulations, pre-flight checks, and accident prevention.
FAA Regulations for Drone Operation
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States regulates drone operation within various airspace classes. These classes, designated by letters (A-G), dictate altitude restrictions, required pilot certifications, and operational limitations. For instance, Class G airspace, typically found in rural areas, allows for more flexibility, while Class B airspace, encompassing major airports, necessitates stricter adherence to regulations and often requires prior authorization.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the intricacies of controlling the drone itself, and for comprehensive guidance on this, you should consult a helpful resource like this guide on how to operate a drone. Proper training ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to successful flights.
Drone Safety Procedures

Safe drone operation involves a structured approach encompassing pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight procedures. A comprehensive checklist ensures all aspects are covered.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage.
- Verify the battery is fully charged and securely connected.
- Check the propellers for damage or looseness.
- Ensure all sensors are clean and functioning correctly.
- Confirm GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Review weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Check for any obstacles in the intended flight area.
- Verify compliance with local and FAA regulations.
Common Drone Accidents and Prevention
Common drone accidents often stem from pilot error, such as loss of control due to strong winds or battery failure. Others include collisions with obstacles or unauthorized entry into restricted airspace. Regular maintenance, thorough pre-flight checks, and adherence to regulations significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
Drone Insurance Options
| Insurance Provider | Coverage | Price Range | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | Liability and damage | $XX – $YY per year | 24/7 support, online claims |
| Provider B | Liability only | $ZZ – $WW per year | Fast claims processing |
| Provider C | Comprehensive coverage | $AA – $BB per year | Worldwide coverage |
Choosing and Setting Up Your Drone
Selecting the right drone and properly setting it up are crucial steps for a successful flight experience. Consider factors like features, budget, and intended use when choosing a drone. The setup process involves charging the battery, installing the app, and calibrating the drone’s sensors.
Drone Model Comparison, How to operate a drone
Drone models vary widely in features, price, and capabilities. Factors to consider include camera quality, flight time, range, GPS capabilities, and ease of use. Researching various models and reading reviews can help you make an informed decision.
Setting Up a New Drone
- Charge the drone’s battery fully before the first flight.
- Download and install the drone’s dedicated mobile application.
- Connect the drone to your mobile device via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors following the app’s guidelines.
- Perform a pre-flight check according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Drone Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibration ensures accurate readings from the drone’s compass and sensors, crucial for stable flight and precise positioning. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, typically involving a series of rotations and movements.
Connecting the Drone to a Mobile Device
Connecting the drone to your mobile device or remote controller usually involves establishing a Wi-Fi connection. The specific steps may vary depending on the drone model and the associated app. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for precise details.
Essential Drone Accessories
- Extra batteries
- Spare propellers
- Carrying case
- Screen protector for mobile device
- Propeller guards (for beginners)
Basic Drone Flight Controls
Understanding basic drone flight controls is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers takeoff, hovering, landing, and basic maneuvers. Mastering these fundamentals builds a solid foundation for more advanced techniques.
Drone Remote Control Functions
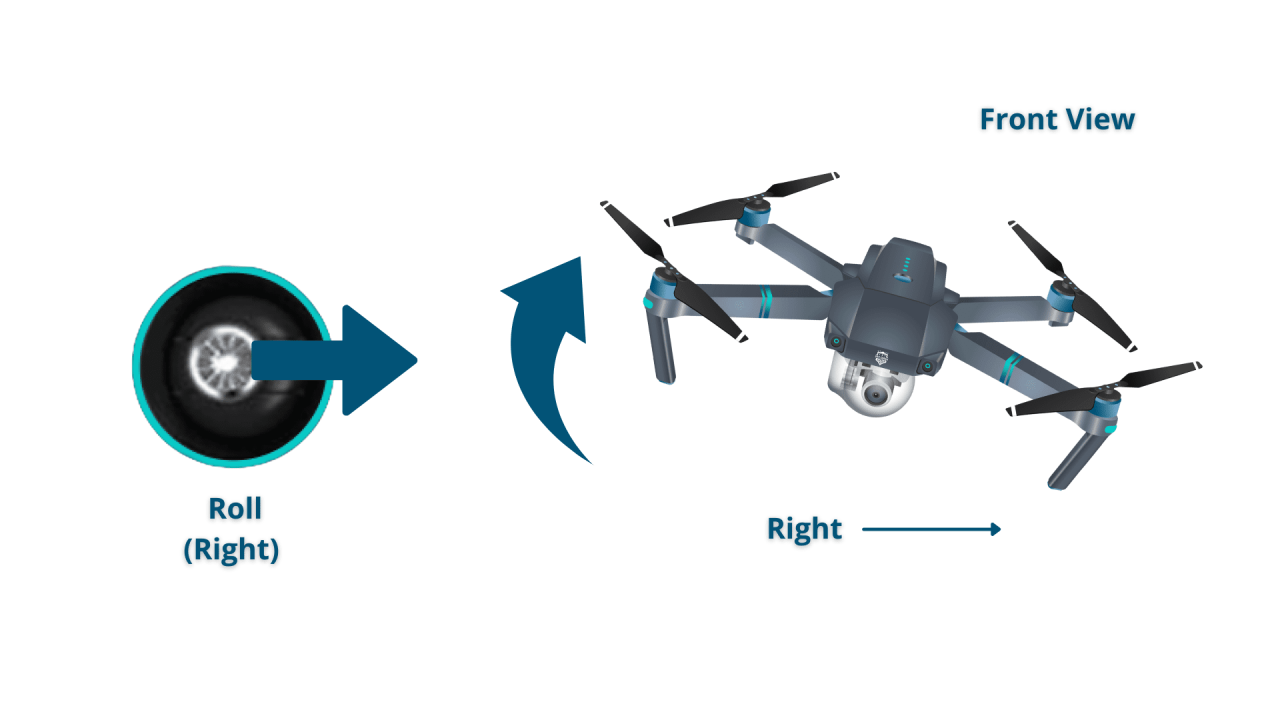
Standard drone remotes typically feature two control sticks (left and right) and various buttons. The left stick generally controls the drone’s altitude and direction, while the right stick controls yaw (rotation) and movement. Buttons control functions like takeoff, landing, camera operation, and return-to-home.
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing Procedures
- Ensure the drone is calibrated and connected to the controller.
- Follow the app’s instructions for takeoff.
- Practice hovering the drone steadily at a low altitude.
- Slowly lower the drone for a controlled landing.
Basic Drone Maneuvers

Basic maneuvers include ascending, descending, turning, and moving forward, backward, and sideways. Practice these movements in a safe, open area to develop smooth and controlled flight.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Maintaining stable flight requires adjusting the controls in response to wind conditions and other external factors. Practice flying in various conditions to build your skills and adapt to changing environments.
Flight Modes Comparison
| Flight Mode | Description | Applications | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness | Training, new pilots | Safer, less challenging |
| Sport Mode | Increased speed and responsiveness | Experienced pilots, dynamic shots | More challenging, higher risk |
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS for precise positioning | Waypoint navigation, autonomous flight | Requires GPS signal |
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once you’ve mastered basic flight controls, you can explore advanced techniques like GPS-assisted flight, complex maneuvers, and advanced camera settings. These techniques enhance your drone’s capabilities and allow for creative aerial photography and videography.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Learning to navigate effectively is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
GPS-Assisted Flight and Waypoint Navigation
GPS allows for autonomous flight and waypoint navigation, enabling you to program a flight path and have the drone follow it automatically. This feature is particularly useful for complex shots or surveying large areas.
Complex Maneuvers (Orbiting and Subject Following)
Advanced drones often offer features like orbiting a point of interest or automatically following a moving subject. These features require practice and understanding of the drone’s capabilities.
Advanced Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for capturing high-quality footage. Experiment with different settings to achieve desired results in various lighting conditions.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Video Recordings
Smooth and stable video recordings are essential for professional-looking footage. Techniques like using gimbal stabilization, flying at a consistent speed and altitude, and post-processing editing contribute to achieving this.
Resources for Advanced Drone Piloting
- Online tutorials and courses
- Drone pilot communities and forums
- Books and manuals on advanced drone techniques
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. This section covers framing shots, using different camera modes, adjusting camera settings, and capturing compelling visuals.
Framing Shots and Composing Scenes
Effective framing involves considering the rule of thirds, leading lines, and the overall composition of the scene. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find the most visually appealing shots.
Using Different Camera Modes
Different camera modes, such as photo, video, and timelapse, offer various creative options. Understanding the strengths of each mode allows you to choose the best option for your desired outcome.
Adjusting Camera Settings (ISO, Shutter Speed, Aperture)
Adjusting ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affects the image’s brightness, sharpness, and depth of field. Understanding how these settings interact is crucial for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Tips for Capturing Stunning Aerial Photography and Videography
Tips include flying at the golden hour for optimal lighting, utilizing natural leading lines, and employing creative camera angles. Post-processing editing can enhance the final product.
Camera Angles and Visual Impact
| Camera Angle | Visual Impact | Suitable Subjects | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Angle | Shows scale and context | Landscapes, cityscapes | Overhead shot of a sprawling landscape |
| Low Angle | Creates a sense of grandeur | Buildings, monuments | Close-up shot of a skyscraper looking upwards |
| Dutch Angle | Adds dynamism and unease | Action scenes, dramatic shots | Tilted shot of a car chase |
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section covers common problems, troubleshooting steps, and basic maintenance procedures.
Common Drone Problems and Causes
Common problems include low battery, signal loss, motor malfunctions, and GPS issues. Identifying the cause is the first step towards resolving the problem.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking different components and settings. Start with simple solutions, such as checking battery levels and signal strength, before proceeding to more complex issues.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Basic maintenance includes cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, checking for loose screws, and replacing worn-out parts. Regular maintenance extends the drone’s lifespan and ensures safe operation.
Safe Drone Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect the drone from damage. Use a carrying case and avoid exposing the drone to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions.
Recommended Tools and Supplies for Drone Maintenance
- Screwdrivers
- Cleaning cloths
- Spare propellers
- Multi-tool
- Battery charger
Drone Flight Planning and Mission Preparation
Careful flight planning and pre-flight checks are essential for successful drone missions. This section covers selecting a flight location, assessing hazards, creating a flight plan, and maximizing battery life.
Importance of Flight Planning and Pre-Flight Checks
Thorough planning and pre-flight checks minimize risks and ensure a smooth flight. This includes considering weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and potential obstacles.
Selecting a Flight Location and Assessing Potential Hazards
Choosing a suitable location involves checking for airspace restrictions, identifying potential obstacles, and considering wind conditions. A safe and open area is crucial for a successful flight.
Creating a Flight Plan Using Drone Software
Drone software allows for creating detailed flight plans, including waypoints, altitudes, and camera settings. This enables precise control over the drone’s movements during the mission.
Maximizing Battery Life and Flight Time
Maximizing battery life involves optimizing flight settings, avoiding extreme maneuvers, and using appropriate batteries for the mission’s duration. Carrying extra batteries is always recommended.
Essential Considerations for Different Types of Drone Missions
| Mission Type | Considerations | Example | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerial Photography | Lighting, composition, camera settings | Capturing landscape images | Avoid flying near people or obstacles |
| Inspection | Access points, weather conditions, close-range flight | Inspecting a bridge | Maintain a safe distance from the structure |
| Videography | Smooth movements, stable platform, subject tracking | Filming a sporting event | Ensure clear airspace and avoid collisions |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation in both, equipping you to navigate the legal landscape, select the appropriate equipment, and execute safe and effective flights. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot. Embrace the challenges, hone your skills, and enjoy the limitless possibilities that await you in the skies.
Helpful Answers
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary significantly depending on the drone model and battery size, but generally range from 15 to 30 minutes.
How do I know if my drone’s battery is fully charged?
Check the battery indicator lights on the drone or in the accompanying app. A full charge is usually indicated by solid lights or a 100% display.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, try to visually locate your drone and attempt to regain control.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced significant magnetic interference.
